Scientific name: *Diospyros rhombifolia* Hemsl.
English name: Crowpersimmon
Family: Ebenaceae (Persimmon family)
Common names: Wild persimmon, Rhombic-leaved persimmon
Morphological characteristics:
This is a deciduous shrub with a thick and tough main root. The branches are slender and often armed with small thorns. The leaves are alternate, ovate to obovate in shape, measuring about 4.5–5.5 cm in length and 2–3 cm in width. The leaf tips are blunt or obtuse, and the base is narrowly wedge-shaped. Flowers are white, solitary, and appear within the leaf blade. They are unisexual and dioecious, meaning male and female flowers occur on separate plants. The fruits are ovoid or oval, with a pointed tip, covered in fine hairs. When mature, they turn orange-yellow and remain on the tree for some time. The sepals are leathery, with prominent straight veins.
Flowering occurs from March to June, and the fruiting season typically begins in October. The bark is brown, smooth, and has distinct branching patterns. The leaves are papery, ranging from ovate to rhombic or obovate, with a blunt tip and a wedge-shaped base. The veins on the underside of the leaves are yellowish, and the surface is mostly hairless, though sparsely hairy on the lower side. The flowers are white and appear singly.
Habitat and distribution:
It grows naturally on sunny hillside slopes, often found in shrublands near villages. Its distribution is sparse across the region.
Native to China, it is found in Fujian, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang provinces. It occurs naturally in these areas without any known cultivation.
Ecological habits:
This plant prefers full sunlight but can tolerate some shade. It thrives in humid climates and grows well in fertile, well-drained soils.
Medicinal parts: Dried roots and branches are used for medicinal purposes.
Greening and use:
The plant is aesthetically pleasing, with smooth, elegant branches. In autumn, its bright orange-yellow fruits hang densely on the trees, adding a vibrant touch to the landscape. Due to its shade tolerance, it is an excellent choice for undergrowth planting in green spaces and as a fruit-bearing species.
The roots and branches are used in traditional medicine to treat liver diseases, jaundice, bruises, and other conditions. The fruit is also used similarly to common persimmons.
Taste and function:
Bitter and astringent in taste, it helps improve blood circulation, nourish the liver, and clear heat from the body.
Indications:
It is used for acute jaundice hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, bruises, and certain types of bone tuberculosis.
Application references:
1. For jaundice hepatitis: 15–30 grams of dried root, decocted in water.
2. For liver cirrhosis: 12 grams of root combined with 6 red dates, decocted in water.
3. For bruises: 30 grams of root, decocted in water.
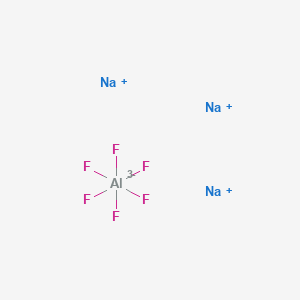
Cryolite Basic Information
CAS: 15096-52-3
MF: AlF6Na3
MW: 209.94
EINECS: 239-148-8
Mol File: 15096-52-3.mol
Cryolite Chemical Properties
Melting point 1012
Boiling point decomp
density 2.9 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
Cryolite Application
Mainly used as aluminum smelting flux, Insecticide, also used in glass, enamel, resin, rubber industry
Chrysolite Gemstone,Chrysolite Stone,Chrysolite Vertus,Cryolife Homograft,Cryolite
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com