Nature: Chinese scientists reveal for the first time why diabetics are prone to cancer
July 23, 2018 Source: Biological Exploration of: exploration bacteria
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];Epidemiological studies have shown that diabetes is associated with an increased risk of cancer. High glucose levels may be a major factor in the association between diabetes and cancer, but we don't know much about the molecular mechanisms involved. Recently, a major scientific research achievement between Professor Shi Yang and Professor Shi Yujiang of Fudan University Biomedical Research Institute has brought an explanation for this issue.
Image source: CC0 Creative Commons
In the early morning of July 19th, "Nature" magazine published the research results of Professor Shi Yang and Professor Shi Yujiang online, entitled "Glucose-regulated phosphorylation of TET2 by AMPK reveals a pathway linking diabetes to cancer". The article reveals the remodulation of the TET2 phosphorylation pathway mediated by the energy receptor AMPK in the process of connecting diabetes and cancer and its related molecular mechanisms, and describes the mechanism by which the "magic drug" metformin inhibits tumors.

New pathway between diabetes and cancer
The TET family of proteins in DNA demethylase is one of the most interesting star proteins in the field of epigenetics in the past 10 years. Three mammals include TET1/2/3, among which TET2 is related to some including tumors. It has been widely concerned with the occurrence and development of diseases.
The TET protein can catalyze the conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC). In cancer cells, a wide decline in the level of 5hmC can be used as a marker to measure the degree of malignancy in cancer.
In this study, the Shi Yujiang team found that high blood sugar levels significantly inhibited the activity of AMPK protein kinases in the body (AMPK is a receptor for important energy in the cell, can sense the level of glucose in the body, and is highly sensitive), and leads to phosphorylation of TET2Ser99. The stability of the protein with TET2 is reduced to reduce the production of 5hmC by TET2 protein. When 5hmC cells are reduced, it means that the possibility of tumorigenesis increases.
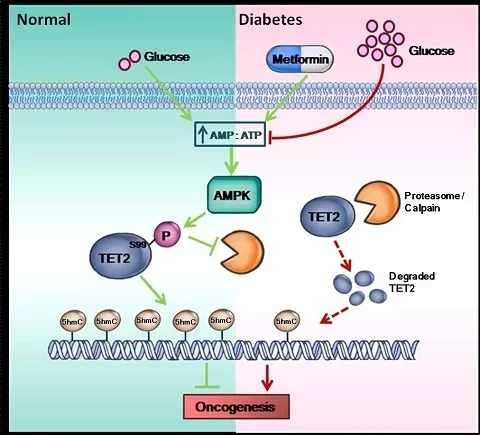
Epigenetic pathways intrinsically associated with diabetes hyperglycemia and cancer (Source: Fudan University's official website)
Metformin anticancer mechanism
Previously, Jun has reported that metformin specifically slows tumor growth by preventing cellular respiration and inhibiting the production of aspartate. In the past, reports on the anti-cancer effect of "Shenzhen" metformin have also emerged endlessly. In this study, the Shi Yujiang team tried to verify the anticancer efficacy of metformin with newly discovered molecular mechanisms.
It was found that metformin inhibited tumor growth by activating AMPK, followed by phosphorylation of downstream TET2, enhanced TET2 stability and its product 5hmC. And the inhibition of metformin depends on the presence of TET2. It is reported that this discovery first reported the interaction between AMPK and TET2, directly linking energy regulation and epigenetic key enzymes, revealing that energy regulation depends on epigenetic regulation.
Overall, this study first discovered the important role of phosphorylation on TET2 protein in regulating intracellular 5hmC and found AMPK, a key regulator of TET2 upstream. From a clinical point of view, although studies have shown that diabetes is closely related to the increased risk of cancer, the molecular basis behind this association is still unclear. This study explains the increased risk of cancer in diabetic patients to some extent in terms of epigenetics. The reason for this is that low levels of 5hmC in diabetic patients may be an important factor in cancer.
References: 1) http://news.fudan.edu.cn/2018/0719/46230.html
2) Glucose-regulated phosphorylation of TET2 by AMPK reveals a pathway linking diabetes to cancer
3) http://
Original title: "Shen medicine" metformin boarded Nature! Chinese scientists reveal for the first time why diabetic patients are susceptible to cancer
Tuna Loin,Frozen Tuna Loin,Fresh Tuna Loin,Yellowfin Tuna Loin
ZHEJIANG RETRONX FOODSTUFF INDUSTRY CO.,LTD , https://www.retronxfoods.com