Azure Biosystems is an innovative company that serves the life sciences, and its imaging products reflect the spirit of innovation, technology and disruption. Based on the original C Series multi-function imaging system, we introduced the Azure Sapphire dual-mode multi-spectral laser imaging system. With dedicated detectors for each channel, PMT for blue and phosphor screen scanning, three independent APD detectors for green, red and near-infrared fluorescence detection, and a CCD detector for ultra-high Sensitive chemiluminescence detection.
 Why is sapphire using exclusive detection for each channel? What are the advantages?
Why is sapphire using exclusive detection for each channel? What are the advantages?

Photomultiplier tubes (PMT) and avalanche photodiodes (APD) are optical components commonly used in scanning imaging systems.
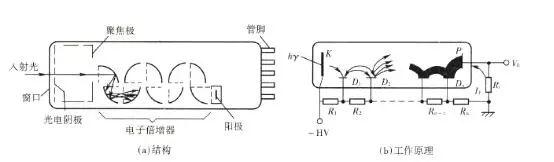
PMT detector: An important product in photonic technology devices, it is a photodetector with extremely high sensitivity and ultra-fast time response. The photomultiplier tube is a vacuum device. It consists of a photoemissive cathode (photocathode) and a focusing electrode, an electron dynode and an electron collector (anode). When light is irradiated onto the photocathode, the photocathode excites photoelectrons into the vacuum. These photoelectrons enter the multiplication system according to the focused electric field and are multiplied by further secondary emission. The amplified electrons are then collected by the anode as a signal output. Because of the secondary emission multiplication system, the PMT is in the range of 300-500 nm, the signal-to-noise ratio is the best, and the quantum conversion efficiency is the largest, but the quantum conversion rate is extremely low in the infrared and near-infrared regions, and the signal-to-noise ratio is low. Therefore, the photomultiplier tube detects blue light in ultraviolet and visible light, and has extremely high sensitivity and extremely low noise (Fig. 1). Sapphire uses a PMT detector in the blue region with high quantum conversion rates for higher sensitivity.

PMT detector
Spectral effect: 300 to 850nm
Maximum quantum conversion efficiency: at 420nm
figure 1
APD detector: is a photosensitive element used in laser communication. After a reverse bias is applied to the PN junction of a photodiode made of silicon or germanium, the incident light is absorbed by the PN junction to form a photocurrent. Increasing the reverse bias produces an "avalanche" (that is, the photocurrent multiplies), so this diode is called an "avalanche photodiode." APD has a higher quantum conversion efficiency and higher sensitivity silicon photodetector than PMT in the 400-1100nm wavelength range, and this extended spectral response can be used to extend the operating wavelength range of the scanning system (Figure 2), APD detection The device is smaller than the vacuum tube PMT, and the APD operating under high voltage bias also has an internal gain mechanism similar to PMT, which produces a large output current for each initial photoelectron. The APD detector features ultra-low noise, high speed, high transimpedance gain, and high sensitivity. It is mainly used for the detection of visible red-green fluorescence and near-infrared fluorescence. Therefore, Sapphire is equipped with three independent APD detectors for long-wavelength detection, better signal-to-noise ratio and higher detection sensitivity. 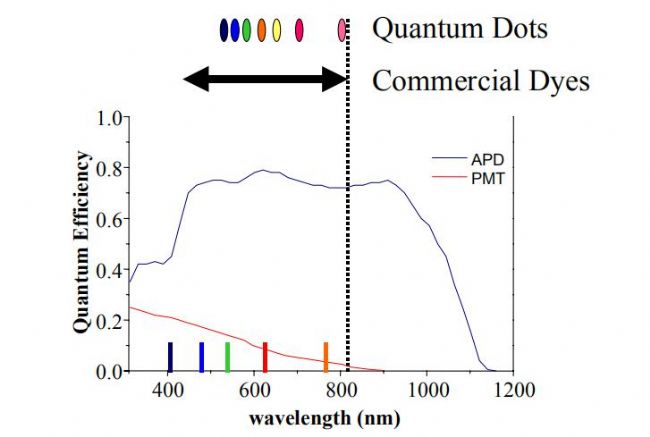
Figure 2. Quantum efficiency of the APD and PMT detectors. The bars on the lower axis indicates the typical excitation wavelengths at 405 nm, 488 nm, 532 nm, 632 nm, and 785 nm. The range of emission wavelengths of commercial dyes and the Emission peaks of the quantum dots are shown at the top of the figure.
("A Comparison of Avalanche Photodiode and Photomultiplier Tube Detectors", William G. Lawrencea, Gyula Varadia, 2008,)
Nowadays, the commercial scanning imaging system only scans a detection and detection method. The sapphire dual-mode multi-spectral laser imaging system has broken the pattern. In addition to the scanning imaging method, sapphire comes standard with 6.1 million pixels and a large aperture. The cold CCD detector performs full-spectrum imaging for highly sensitive chemiluminescence detection. Because chemiluminescence is a process of signal accumulation, if imaging is performed using a scanning method, the signal is not synchronized for imaging, and the signal loss is severe.
A CCD (Charge Coupled Device) is a charge coupled device image sensor. It is made of a high-sensitivity semiconductor material that converts light into electric charge and converts it into a digital signal through an analog-to-digital converter chip. It can easily transfer data to a computer, and by means of computer processing, as needed And imagine to modify the image. A CCD consists of many photosensitive units, usually in megapixels. When the CCD surface is exposed to light, each photosensitive unit reflects the charge on the component, and the signals generated by all the photosensitive units are added together to form a complete picture.
 Azure Sapphire gives customers three detectors so that their samples are not missing in any extreme detection environment. Achieve unparalleled sensitivity and access to high quality images.
Azure Sapphire gives customers three detectors so that their samples are not missing in any extreme detection environment. Achieve unparalleled sensitivity and access to high quality images.
Fashion Leggings,Summer Leggings,Leggings For Women,Stretch Yoga Leggings
Xinhui Jielide Garment Factory , https://www.ntgfwear.com